
Molecular electrocatalysts are regarded as a promising alternative for the electrolysis of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) through two-electron oxygen reduction reaction (2e-ORR). Oxygen-functionalized groups (OFGs) on the carbon supports are proven to have great influence on the molecular center. However, such catalysts are always limited by their poor electrocatalytic activity and durability in acidic solutions, and little work has been done to investigate the interaction mechanism when the specific OFG interacts with the active center.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. YANG Hui from Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a strategy to promote H2O2 selectivity by designing a cobalt porphyrin supported on reduced graphene oxide molecular catalyst (CoTPP@RGO), which enabled the stable electrosynthesis of H2O2 at industrial-scale current in proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzer.
The results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
In the study, scientists tailored the variation of the single OFG on the reduced graphene oxide (RGO) carrier at the specific temperature and prepared several CoTPP@RGO-T catalysts.
Advanced characterization techniques combined with density functional theory calculations revealed the regulation effects of different OFGs on the electronic structure of the active center and unraveled the enhancement mechanism of 2e-ORR activity on the developed CoTPP@RGO catalyst.
It was found that PEM electrolyzer with the CoTPP@RGO-160 catalyst could continuously produce pure H2O2 aqueous solution with a high concentration of up to ca. 7 wt% at 400 mA cm-2 over 200 h with a low cell voltage of ~2.1 V, demonstrating the breakthrough of exceptional stability.
The findings provided a new strategy for the rational design of the active centers for molecular catalysts, highlighting the enormous potential of supported molecular catalysts for the electrosynthesis of H2O2 in an acidic environment as well as its application in industrial-scale H2O2 electrosynthesis.
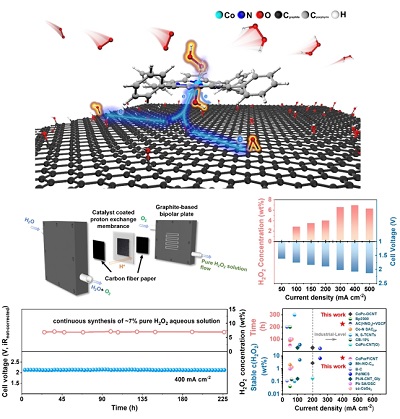
Interaction mechanism investigation and PEM performance evaluation. (Image by SARI)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

